PC Cooling System: Keeping Your Computer Cool and Efficient
The cooling system in a computer is responsible for maintaining safe operating temperatures for all internal components. When you play games, render videos, or run heavy applications, components like the CPU and GPU generate heat. Without proper cooling, this heat can cause your system to throttle performance, crash, or even damage hardware. A good cooling system ensures stability, longevity, and optimal performance.
→ Video: How PC Cooling Works
This video explains the basics of how computer cooling systems function and why they’re so important:
→ Why Cooling Matters
- Performance: Prevents thermal throttling, ensuring your CPU and GPU run at full speed.
- Component Lifespan: Lower temperatures increase hardware durability and stability.
- System Noise: Efficient cooling keeps fans quieter.
- Overclocking: Essential for safely pushing your CPU or GPU beyond factory speeds.
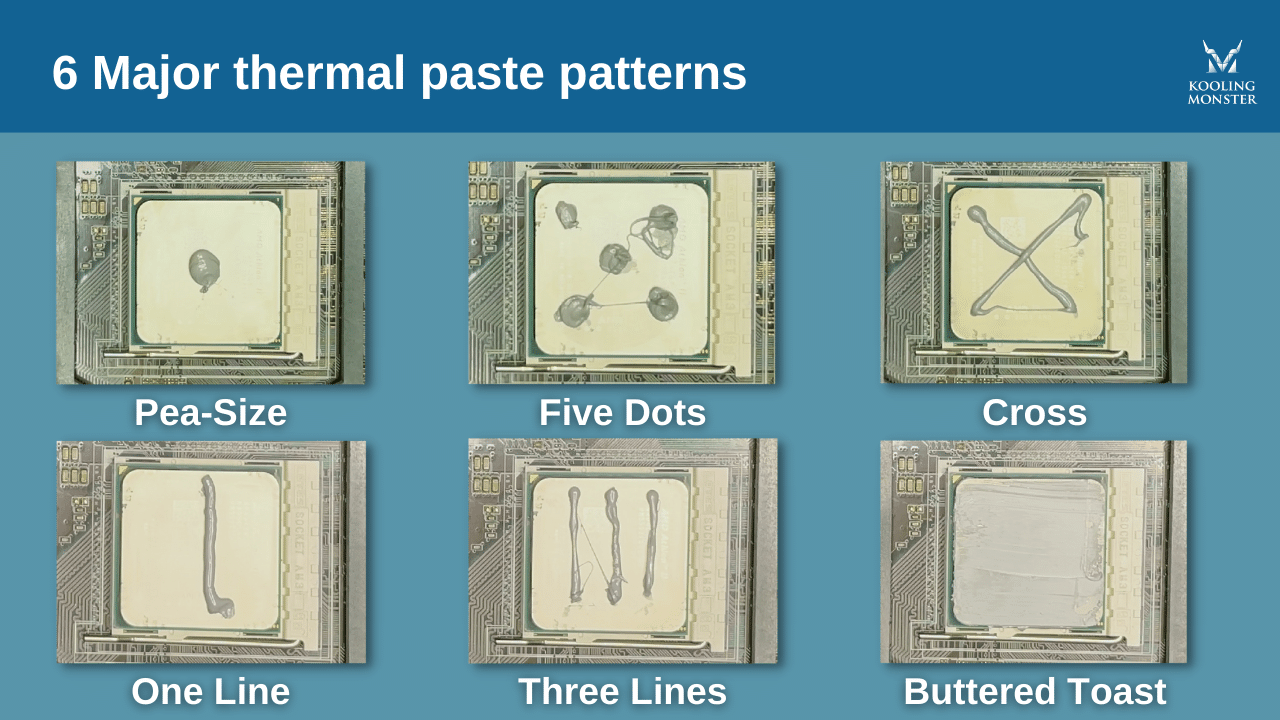
→ Thermal Paste and Its Importance
Thermal paste (also called thermal compound) is a special material applied between the CPU or GPU and the cooler’s base. Its main purpose is to fill microscopic gaps, ensuring maximum heat transfer between surfaces.
- Always apply a small, even amount — too much can reduce efficiency.
- Replace every 1–2 years for optimal thermal performance.
- High-end pastes use materials like silver or liquid metal for better conductivity.
→ Main Types of Cooling Systems
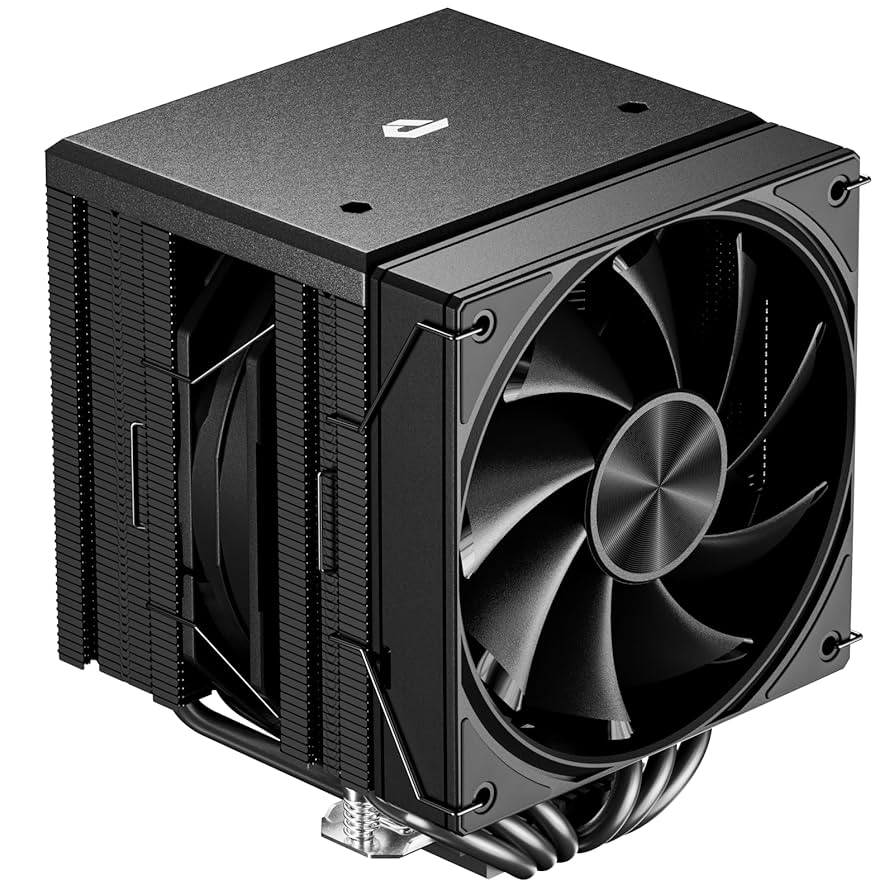
1. Air Cooling
Air cooling is the most common and affordable method. It uses fans and heat sinks to draw heat away from the CPU or GPU and push it out of the case.
- Uses metal heat sinks (usually aluminum or copper).
- Includes one or more fans to move air through the case.
- Requires good case airflow to be effective.
- Quiet, reliable, and low maintenance.
2. Liquid Cooling (AIO / Custom Loop)
Liquid cooling uses a special fluid to transfer heat away from components through tubes and radiators. It is more efficient than air cooling and ideal for high-performance or gaming PCs.
- AIO (All-In-One) Coolers: Pre-assembled, easy to install, with a pump, radiator, and fans.
- Custom Water Loops: Fully customizable cooling systems used in enthusiast builds.
- Offers better heat dissipation and a cleaner look.
- Requires more maintenance than air cooling.
3. Passive Cooling
Passive cooling uses no fans. It relies on heat sinks and natural airflow. It’s completely silent but only suitable for low-power systems like small form factor PCs or embedded devices.
- Zero noise and no moving parts.
- Limited cooling capability — not for gaming PCs.
- Ideal for home servers or HTPCs.
→ Key Cooling Components
- Heat Sink: Metal block that absorbs heat from the CPU/GPU.
- Fans: Move air across heat sinks and through the case.
- Thermal Paste: Improves heat transfer between CPU and cooler.
- Radiator (for liquid cooling): Dissipates heat from the liquid into the air.
- Pump (for liquid cooling): Circulates coolant through the system.
- Case Airflow: Proper intake and exhaust fans ensure balanced cooling.
→ Comparison: Air Cooling vs Liquid Cooling
| Feature | Air Cooling | Liquid Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good | Excellent |
| Noise Level | Moderate | Low (depends on fans) |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Medium (check pump, coolant) |
| Cost | Budget-friendly | More expensive |
| Best For | Casual & mid-range PCs | Gaming & high-performance builds |
→ Tips for Better Cooling
- Use quality thermal paste and apply it properly on the CPU.
- Ensure good case airflow — intake from the front, exhaust at the rear or top.
- Clean dust filters and fans regularly.
- Replace noisy or old fans with PWM-controlled fans for quieter operation.
- Consider upgrading to liquid cooling for overclocked or high-performance systems.
→ Maintenance Tips for Cooling Systems
- Clean fans and dust filters every few months to maintain airflow.
- Check temperatures regularly with monitoring tools like HWMonitor or MSI Afterburner.
- Ensure cables are properly managed to avoid blocking airflow.
- For liquid cooling: replace coolant every 12–18 months and check for leaks or pump noise.
→ Conclusion
The cooling system is the unsung hero of your PC. It keeps temperatures under control, ensures your components run efficiently, and prevents costly damage. Whether you prefer a simple air cooler or a custom liquid loop, proper cooling will make your system more stable, quieter, and longer-lasting. A well-cooled PC is a healthy PC!
👉Click here to return to the main page of this blog: GENERAL PAGE






No comments:
Post a Comment