Power Supply Unit (PSU): Complete Guide for Your PC Build
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) is the heart of your PC, providing electricity to every component from the motherboard and CPU to the GPU, storage drives, and fans. A high-quality PSU ensures stability, efficiency, and protection, preventing damage to expensive components. Choosing the right PSU is crucial for reliability and future-proofing your system.
→ Video: How a PSU Works
This video explains PSU fundamentals, efficiency ratings:
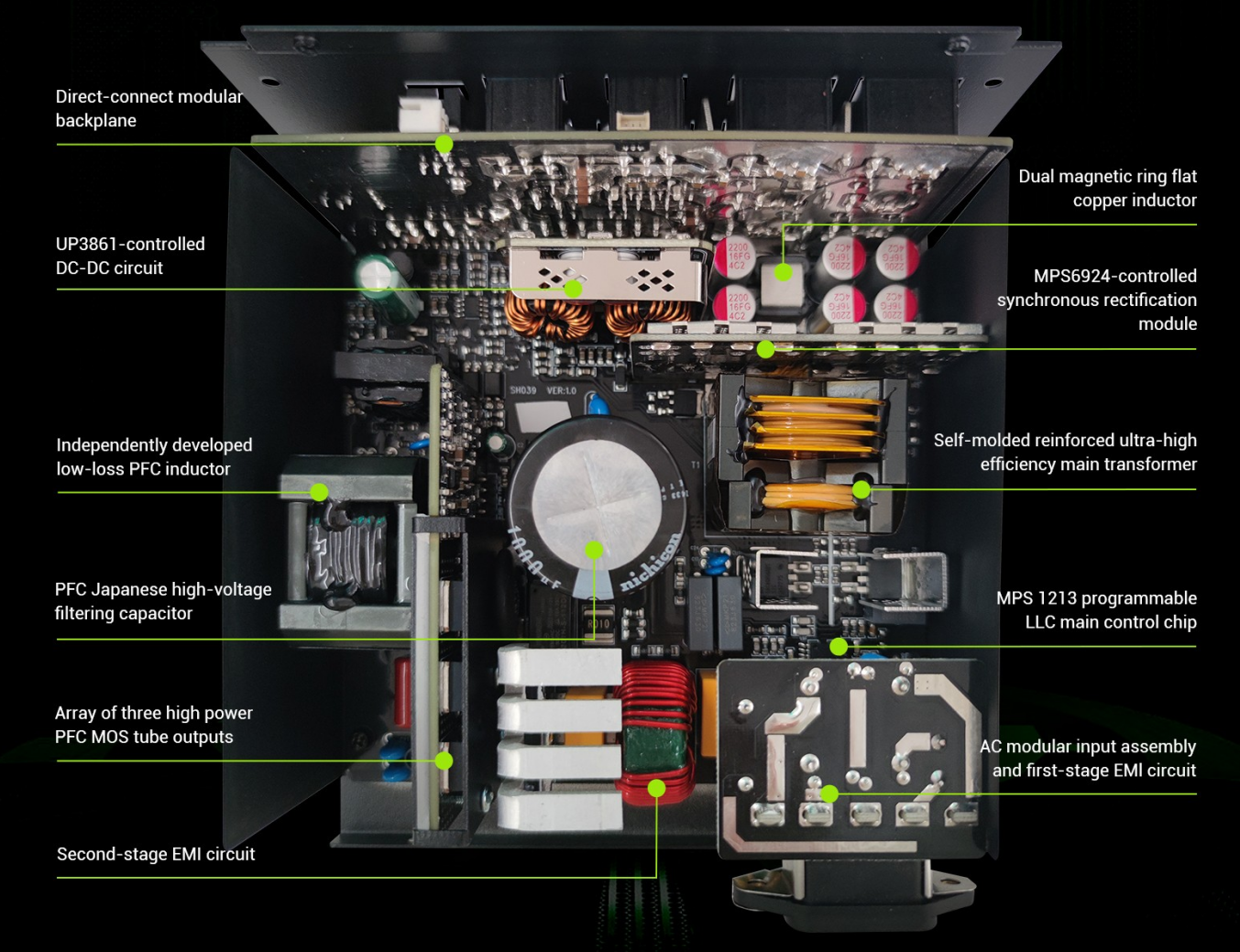
→ Main Parts of a PSU
- AC to DC Conversion Circuit: Converts wall power into usable DC voltage for the PC.
- Transformers & Capacitors: Stabilize voltage and smooth electrical flow.
- Cooling System: Fan or passive cooling to prevent overheating.
- Cables & Connectors: Power to motherboard (24-pin), CPU (4/8-pin), GPU (6/8/12-pin), SATA drives, and peripherals.
- Protective Circuits: Overvoltage, overcurrent, short circuit, and overtemperature protection.
- PSU Housing: The metal enclosure that keeps components secure and allows airflow.
→ Types of PSUs
1. Non-Modular PSU
- All cables permanently attached.
- Cheaper but harder for cable management.
- Good for budget builds.
2. Semi-Modular PSU
- Main cables fixed (24-pin, CPU), others detachable.
- Better cable management than non-modular, still affordable.
3. Fully Modular PSU
- All cables removable.
- Maximum flexibility and airflow, best for high-end builds.
→ Important Specifications
- Wattage: Total power output. Ensure enough for CPU, GPU, and peripherals plus 20–30% headroom.
- Efficiency Rating (80 PLUS): Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, Titanium — higher rating = less wasted energy.
- Form Factor: ATX (most common), SFX (small cases), TFX, etc.
- Rails: Single vs multiple +12V rails. Most modern high-quality PSUs have strong single rail.
- Protections: OVP, OCP, SCP, OTP, ensuring safety for all components.
- Cooling: Fan size, airflow direction, or passive cooling affects noise and temperature.
→ Common Connectors
- 24-pin ATX: Powers the motherboard.
- 4/8-pin EPS: Powers the CPU.
- 6/8-pin PCIe: Powers GPUs.
- SATA power: Powers SSDs, HDDs, and optical drives.
- Molex: Powers older peripherals and fans.
→ Efficiency Rating Table
| Rating | Efficiency at 50% Load | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| 80 PLUS Bronze | ~85% | Budget & office PCs |
| 80 PLUS Gold | ~90% | Gaming & mid-high builds |
| 80 PLUS Platinum | ~92% | High-performance and workstations |
| 80 PLUS Titanium | ~94% | Extreme efficiency & server builds |
→ How to Choose the Right PSU
- Calculate Total Wattage: Add CPU, GPU, storage, fans, and leave headroom.
- Consider Efficiency: Higher efficiency reduces electricity cost and heat.
- Modular vs Non-Modular: Modular improves airflow and makes cable management easier.
- Brand & Reliability: Stick to Seasonic, Corsair, EVGA, be quiet!, Cooler Master.
- Future Proofing: Choose slightly higher wattage for upgrades or overclocking.
→ Conclusion
The PSU is the lifeline of your PC. A high-quality power supply ensures that every component receives stable and clean power, reduces wasted energy, and protects your hardware. Whether building a budget PC or a high-end gaming/workstation system, investing in a good PSU is essential for stability, longevity, and peace of mind.




No comments:
Post a Comment